In modern data centers, high-speed interconnects are critical to ensuring fast, stable communication between servers, switches, and storage devices. Among the most widely adopted options are AOC (Active Optical Cable) and DAC (Direct Attach Copper Cable). While they may serve similar roles in short-distance transmission, their construction, performance, and application scenarios are quite different.
So, what exactly is the difference between AOC and DAC?

Basic Structure and Transmission Medium
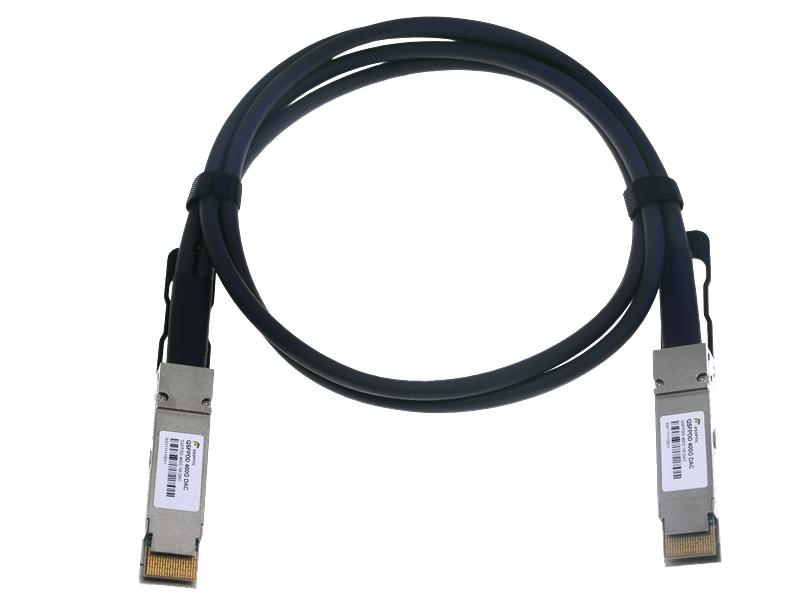
At their core, DAC cables use copper as the transmission medium. They are typically passive, meaning they don’t have any electronic components. Some versions (active DACs) include signal conditioning chips to enhance performance over slightly longer distances.
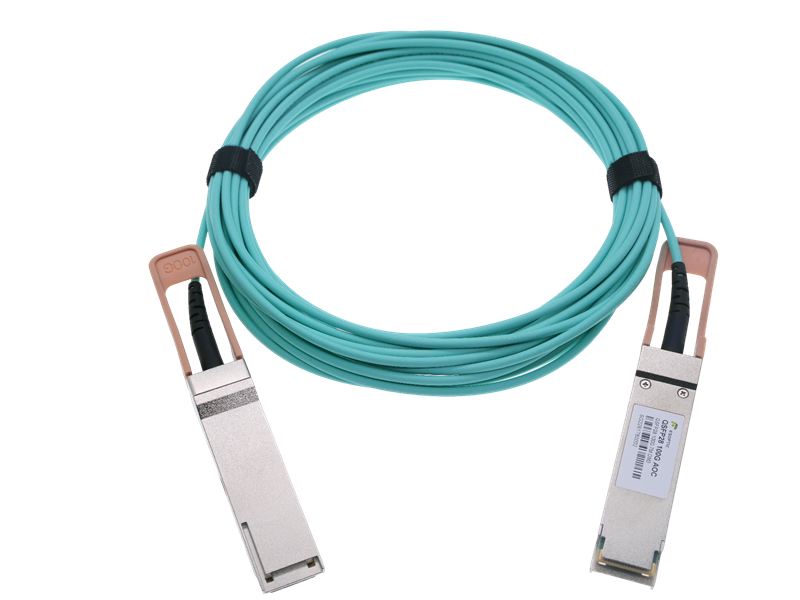
On the other hand, AOC uses optical fiber and contains integrated optical transceivers at both ends. These transceivers convert electrical signals into optical signals and back again, enabling high-speed transmission over longer distances with less interference.
This fundamental difference—copper vs. fiber—defines much of the difference between AOC and DAC in terms of performance and use cases.
Performance and Distance
DAC is commonly used for short-range connections, typically up to 7 meters. It is cost-effective, low in power consumption, and very easy to install.
AOC, however, is designed for longer reach—up to 100 meters or more, depending on the type. It provides superior signal integrity and lower electromagnetic interference (EMI), making it ideal for dense, high-speed environments.
At ESOPTIC, we provide both AOC and DAC solutions optimized for various data center architectures, from 10G to 800G. Whether you're building a high-frequency trading platform or scaling cloud infrastructure, our interconnects ensure stable and efficient data transmission.


Power Consumption and Flexibility
Since AOC has active components, it does consume more power than passive DACs. However, the power cost is offset by the advantages in flexibility and distance. AOCs are lighter, easier to bend, and better suited for high-density cabling environments.
DACs, while rigid and heavier, are often favored for their simplicity and lower price point in Top-of-Rack (ToR) configurations.


FAQs
1. Which is better for short-distance server-to-switch connections?
DAC is generally more economical and effective for connections under 5-7 meters.
2. Is AOC compatible with all switches?
Yes, as long as the transceivers are compatible with the switch ports and protocols.
3. Can I use AOC and DAC interchangeably?
Not always. Their physical properties and performance differ. Choosing between them depends on your network's layout and bandwidth needs.
4. Which cable is more flexible for tight bends?
AOC, being fiber-based, is much more flexible and lighter than DAC.
5. What makes ESOPTIC’s AOC and DAC products different?
ESOPTIC ensures strict quality control, wide compatibility, and excellent after-sales support—making our AOC and DAC solutions reliable choices for any high-speed interconnect need.